UDMA
The Ultra DMA (Ultra Direct Memory Access, UDMA) modes were the fastest method used to transfer data through the ATA hard disk interface, usually between the computer and an ATA device. UDMA succeeded Single/Multiword DMA as the interface of choice between ATA devices and the computer. There are eight different UDMA modes, ranging from 0 to 6 for ATA (0 to 7 for CompactFlash), each with its own timing.
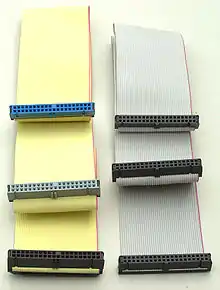
80-conductor cable used for modes faster than UDMA 2 on the left compared to a 40-conductor cable
Modes faster than UDMA mode 2 require an 80-conductor cable to reduce data settling times, lower impedance and reduce crosstalk.[1]
| Mode | Number | Also called | Maximum transfer rate (MB/s) | Minimum cycle time | Defining standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra DMA | 0 | 16.7 | 120 ns | ATA-4 | |
| 1 | 25.0 | 80 ns | ATA-4 | ||
| 2 | Ultra ATA/33 | 33.3 | 60 ns | ATA-4 | |
| 3[2] | 44.4 | 45 ns | ATA-5 | ||
| 4[2] | Ultra ATA/66 | 66.7 | 30 ns | ATA-5 | |
| 5[2] | Ultra ATA/100 | 100 | 20 ns | ATA-6 | |
| 6[2] | Ultra ATA/133 | 133 | 15 ns | ATA-7 | |
| 7 | Ultra ATA/167 | 167 | 12 ns | CompactFlash 6.0[3] |
See also
- PIO—The first interface type used between devices (mainly hard disks) and the computer.
- Parallel ATA
- Serial ATA
References
- AT Attachment with Packet Interface - 7 Volume 2 - Parallel Transport Protocols and Physical Interconnect (ATA/ATAPI-7 V2) E.2.1.1 Cabling p172
- 80-conductor cable required
- CompactFlash 6.0 Introduction Archived 2010-11-21 at the Wayback Machine
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.