I just updated one of my SAM-normalisation tools to more accurately normalise mapped reads to a target coverage. It uses reservoir sampling on a SAM-formatted file to choose reads to bring the coverage up to 100X (if possible).
https://gitlab.com/gringer/bioinfscripts/blob/master/samNormalise.pl
Example Usage:
samtools view -h input.bam | ~/scripts/samNormalise.pl | samtools view -b > normalised.bam
The output BAM file can be converted into a fastq file using 'samtools fastq':
samtools fastq normalised.bam > normalised.fastq
Here are some example before and after shots ['samtools mpileup input.bam'; 'samtools mpileup normalised.bam']:
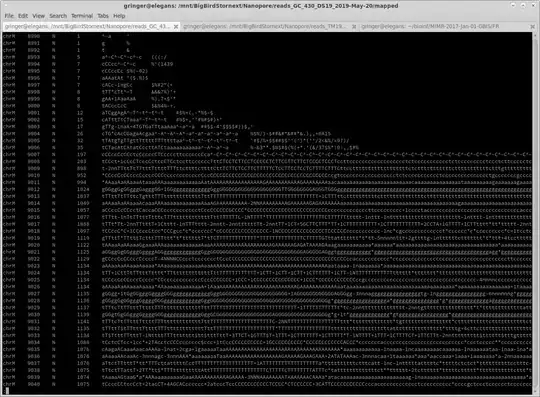
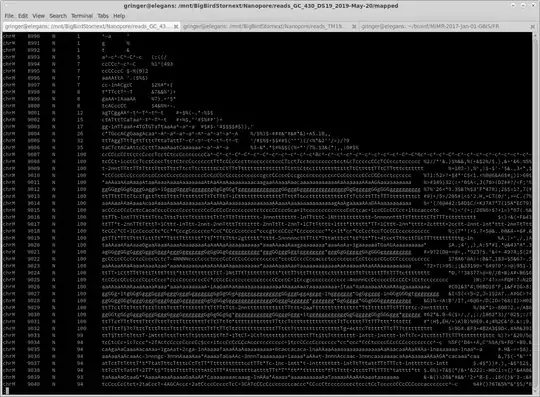
Notice that where the coverage is below 100, the coverage is identical. Coverage is below 100 in some areas because some reads end, and no additional reads start until later on in the reference sequence.
The options are coded as variables at the beginning of the script at the moment, but I can easily convert them to command-line options in the future if there's demand for it.
This will work for long reads (i.e. PacBio, Nanopore), bearing in mind that there may be more low-coverage gaps if the reads are sparsely placed.
As implemented, this won't work properly with paired reads and will leave behind singletons.

